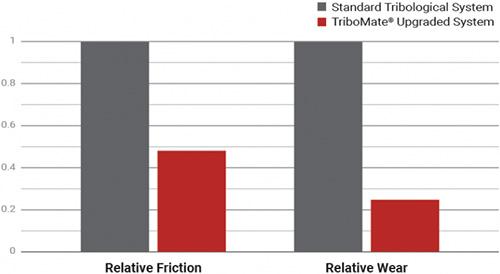
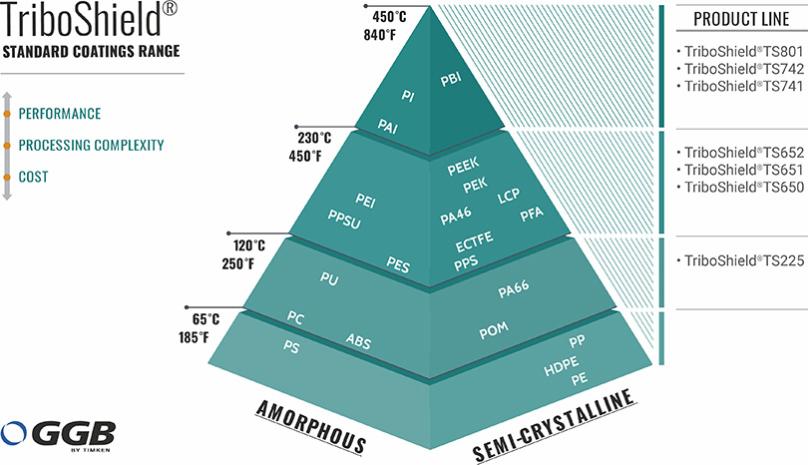
Polymer coatings are thin layers of polymer applied to either flat or irregular substrates. Polymeric coatings can be functional, protective or decorative. They are also used to modify surfaces (paper coatings, hydrophobic coatings). Although polymeric coatings are mostly organic, they can also include ceramic or metal particles to increase durability, functionality, or aesthetics [1].
Applications often require a combination of bulk and surface properties at different locations, timing and in a function of the circumstances. Polymer coatings are often used to modify the substrate surface properties and enhance their performance. Therefore, coatings have become a key branch of the tribological materials science.
[1] Francis, L. F., & Roberts, C. C. (2016). Chapter 6-Dispersion and Solution Processes. Materials Processing.